Sino-Swiss Cooperation on Air Pollution Source Apportionment for Better Air
SAP Title: “Clean Air China: CAC”

Project Brief
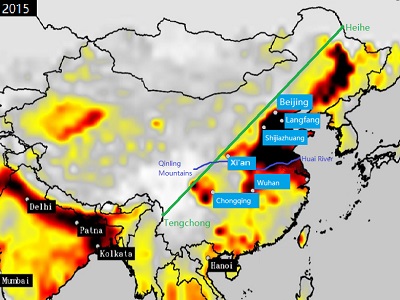
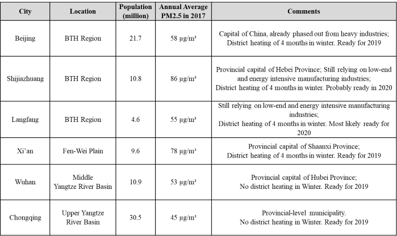
Reduction of air pollution remains of one the highest priority for the government of China. Further improvements in Chinese air quality require information-based decision-making and optimization of mitigation strategies. The project supports these objectives through the application of advanced source apportionment of PM2.5 by rapid analysis of on-line measurement data in 6 pilot cities (Beijing, Shijiazhuang, Langfang, Xi’an, Wuhan, and Chongqing) and assessment of current emission inventories.
The project includes short-term campaigns in a subset of pilot cities. These short-term campaigns utilize state-of-the-art scientific instrumentation beyond that required for the long-term source apportionment analysis to obtain the source-related data needed to initialize, calibrate and perform the source apportionment in the six cities using the monitoring instruments. These long-term data is per se a novelty in China at this moment. In parallel to the on-line measurements, off-line samples will be taken to derive classic and more recent state-of-the-art markers for different sources which can be used to validate the source apportionment at the six sites. Finally, interaction free models shall be developed to derive the PM2.5 sources quickly after measurements for the six cities individually and ideally for all stations together as a generalized model that may be used for the same and additional locations in the future. The data shall be used to understand major gaps in current emission inventories using inverse modelling. Altogether the results shall be used to influence policies regarding air pollution reductions in China.

Project Objectives
(SOURCE APPORTIONMENT) The Capacity of Chinese cities to do accurate air pollutant source apportionment is improved.
Output 1 High-quality data of air pollutants is generated using the new combination of equipment in the six pilot cities.
Output 2 Accurate and timely air pollutants source apportionment results are available for the six pilot cities.
Output 3 Methodologies of new source apportionment model are shared beyond the six pilot cities.
(EMISSION INVENTORY) Timely and reliable air pollutant emission inventory of Chinese cities becomes available.
Output 1 The existing air pollutant inventories in the six pilot cities are updated.
Output 2 Air quality modelling is used to adjust inventory data.
(POLICY INFLUENCE) The results of source apportionment and emission inventory are taken into account for policy making.
Output 1 Policy recommendations are delivered to local and national government through reports and discussed in meetings.
Output 2 Swiss experience of science-based policy making is shared with Chinese government.
(KNOWLEDGE SHARING) The knowledge and experience developed by the Project are effectively disseminated and used.
Output 1 Webpage, newsletter and publications are produced.
Output 2 Project results and experience are shared with other counties and in global events.
Output 3 Health impact study based on the source apportionment results is conducted.

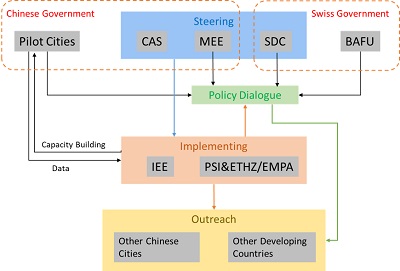
Implementing Strategy
Activity 1.1 Development of the real-time observation system including elemental, inorganic, carbonaceous components based on core equipment (ToF-ACSM/Aethalometer AE33/Xact625i and conduct field observations after training of operators in the six pilot cities. Special campaigns adding ToF-AMS and Extractive Electrospray Ionization (EESI) Mass Spectrometry measurements. Two stations and including two seasons shall be covered. Off-line analysis of filters (around 80-100 per site).
Activity 1.2 Source apportionment of particulate matter using on-line monitoring and campaign data performed in activities 1.1. Source apportionment of particulate matter using off-line measurements and validation of on-line source apportionment.
Activity 1.3 Development of city specific timely source apportionment models. Assessment of uncertainties using the results of Outputs 1.2. Development of a combined model for all cities.
Activity 1.4 Measurements of the health relevant Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS; including DTT, Ascorbic Acid, DFCH).
Activity 2.1 Evaluate and process the existing emission inventories to generate the a priori information for the top-down updates. Generate the source-receptor sensitivity matrix for the precursors and the particulate matter from different emission sectors.
Activity 2.2 Utilize chemical transport model to provide additional information of the spatially and temporally resolved contributions from different regions and sources. Develop ensemble computational scheme based on CMAQ chemical transport model for the pilot cities and aerosol data assimilation method to improve the numerical air quality prediction.
Activity 3.1.1 Deliver the Source apportionment results to local EPA and other governmental agencies. Summarize the source apportionment works at six cities and present consultant technical reports to the Ministry of Ecology and Environment (MEE).
Activity 3.2 Hold training technical workshops, user meetings, academic seminar, etc. to promote the application of Swiss experience and RSA methodology at six pilot cites and other Chinese cities. More special activities will be held during the course of project implementation.
Activity 4.1.1 Develop webpage with Chinese and English languages and release the project progress newsletter quarterly. Organize Sino-Swiss workshop every year to exchange updated results. Publish joint high quality English papers and Chinese monograph to enlarge impact of the project.
Activity 4.2 Initiate a platform for introducing the Chinese and Swiss experience in air pollution control to the developing countries included through the One Belt One Road Initiative. Participate in international events, such as, seminars and conferences to disseminate the project results.